Extraction plants
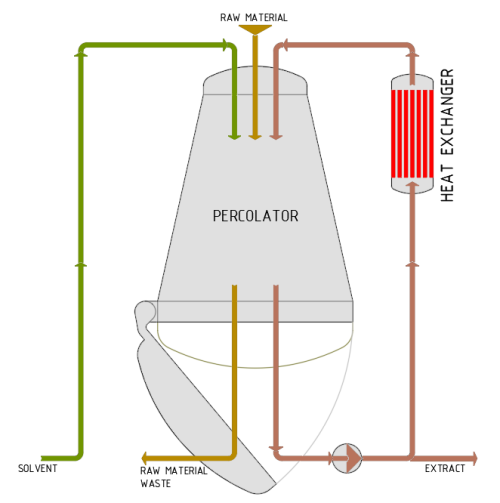
Percolation
SCHRADER extraction plants
Extraction is any separation process in which a (solid, liquid or gaseous) solvent is used to extract one or more components from a natural raw material, the extraction material. The extracted substance is called an extract. The substances to be extracted dissolve better in the solvent than in the raw material. The substances to be extracted can be solve with the solvent from the raw material. In addition, pressure and temperature usually increase the dissolve of substances significantly. SCHRADER uses mainly vegetable and animal raw materials such as vanilla, liquorice, curcuma or bacon in the extraction process and various alcohol-water mixtures as solvents.
In SCHRADER extraction plants, for example, vanilla extracts are obtained from vanilla pod using an ethanol-water mixture as the solvent. A heated ethanol-water mixture is circulated through the vanilla pod for a certain period of time, allowing this to absorb the aromatic components in the vanilla. The vanilla extract produced during this process can be further treated in downstream SCHRADER distillation or evaporation plants, while the ethanol can be recovered in SCHRADER rectification plants.
SCHRADER Pilot Extraction PEx
The SCHRADER Pilot Extraction is designed as a compact experimental plant in pilot scale, both for the research and development of new processes as well for the production of small batches.
The SCHRADER PEx is mounted on a stainless-steel frame, internally hard-wired and piped and is therefore immediately ready for use after connection to the media supply.
A distinction is made between various extraction processes, indicating first the aggregate state of the substance to be extracted and then that of the solvent:
Soxhlet
Percolation
Solid-liquid extraction process
Maceration
Steam distillation
Percolation
Physical process for obtaining liquid plant extracts by passing a solvent through them. Often, an organic solvent or water is passed through plants or plant components.
Maceration
Physical process for softening plant or animal tissue by means of prolonged exposure to liquids such as water, alcohol or oil. Here, only the soluble components of the tissue are transferred to the solvent. The choice of solvent depends on the solubility of the substances to be dissolved.
Steam distillation
Physical separation process to separate or purify volatile substances that are insoluble in water, e.g. oils or aromatics.
Soxhlet
Soxhlet extraction is a continuous physical process used to extract soluble ingredients from solids. The siphon mechanism acts like a Pythagorean cup to continuously draw off the extract, while the extracted material is extracted with pure solvent. The solvent mixture is then evaporated, whereby the solvent is returned to the solids and the extract is enriched.
SCHRADER extraction plants for the
Food industry
Extraction of flavours, colours, vitamins or other nutritional additives from natural raw materials (vegetable or animal) using alcoholic solvents. The enriched extract is obtained from the resulting mixture of dissolved substances and solvent by distilling off the solvent.
Pharmaceutical industry
Extraction of ingredients from medicinal plants for the production of pharmaceuticals or cosmetics. Many herbal medicines contain only dried plant components or extracts thereof. A complex, multi-stage extraction and purification process is required to produce an extract, in the course of which the desired constituents are enriched and undesired constituents are removed. The composition and quantity of these constituents are standardised to ensure consistent quality.
Perfume and cosmetics industry
Fragrances and active ingredients are obtained by extraction. Rose oil, for example, is produced from rose petals by steam distillation, while aloe vera for creams is obtained by means of extraction with hot water from aloe vera plants.
All SCHRADER extraction plants are built to customer specifications, up to the construction of turnkey plants.
Each system can be optionally extended by:
- a distillation plant
- an evaporation plant
- a rectification plant
- a sterilisation plant
- a CIP system
- a tank farm management system
Extraction plant construction types
- Batch extraction process
- Multi-stage semi-continuous extraction processes
- Carousel extraction as a continuous extraction process (suitable only for mono-products and large batches)
Contact
Our global network of experienced engineers is available to you by phone or e-mail. Don’t hesitate to get in touch.




